Often times we come to a situation where we have to search 100 000+ records from local database (coredata or realm) or from a file or a plist etc.
And when user starts to search, each key press will make the call to method that queries this large data resulting in unresponsive app.
One way to optimise this will be implementing debounce.
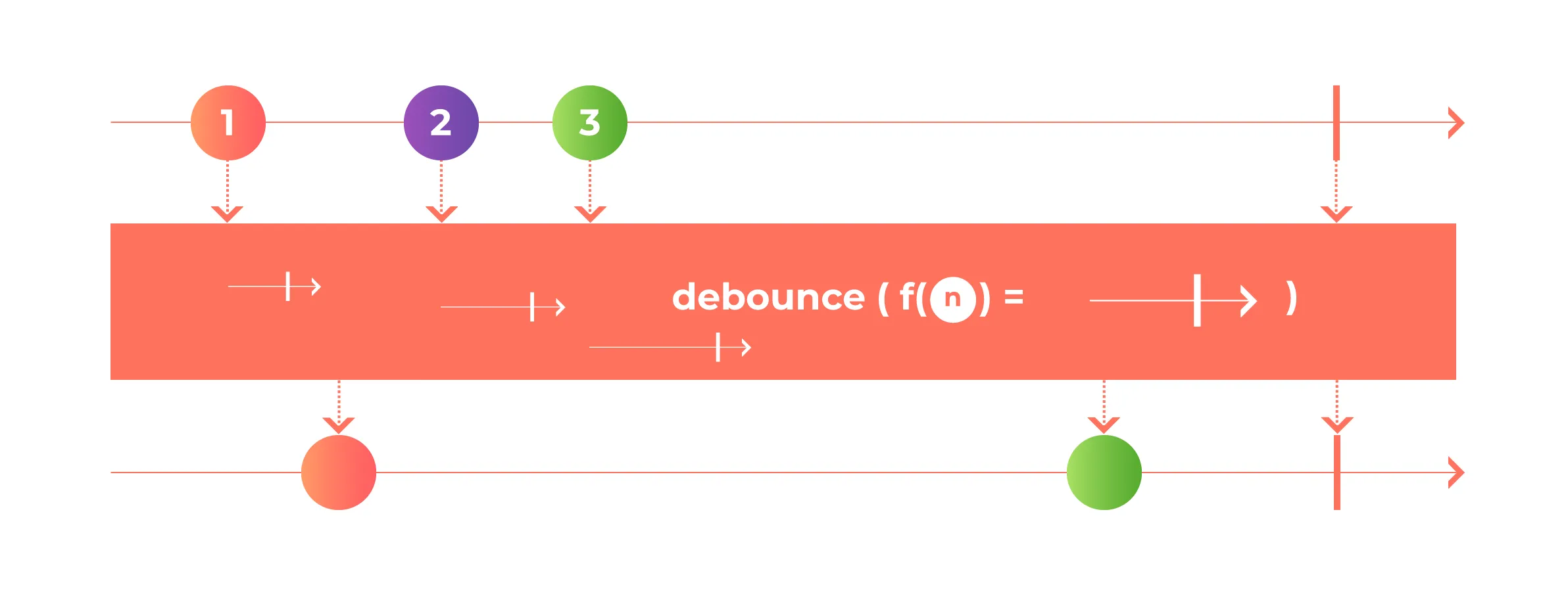
What is debounce?
Its a function which forces the execution to wait a certain amount of time before running again.
We have 4(may be more) ways to achieve debounce in Swift
Timer
Timers are a great way to run code on a repeating basis, and iOS has the Timer class to handle it.
var searchTimer: Timer?
func updateSearchResults(for searchController: UISearchController) {
//Invalidate and Reinitialise
self.searchTimer?.invalidate()
guard let searchText = searchController.searchBar.text else { return }
searchTimer = Timer.scheduledTimer(withTimeInterval: 0.5, repeats: false, block: { [weak self] (timer) in
DispatchQueue.global(qos: .userInteractive).async { [weak self] in
//Use search text and perform the query
DispatchQueue.main.async {
//Update UI
}
}
})
}updateSearchResults is the UISearchController delegate method which gets called on each key press.
searchTimer is an instance variable to store the Timer, Timer is scheduled to execute the closure for 0.5s but if the method gets called before that, then the timer is invalidated and reinitialised.
DispatchWorkItem
A DispatchWorkItem encapsulates work to be performed on a dispatch queue or within a dispatch group.
var searchTask: DispatchWorkItem?
//SearchController delegate method
func updateSearchResults(for searchController: UISearchController) {
guard let searchText = searchController.searchBar.text else { return }
//Invalidate and reinitiate
self.searchTask?.cancel()
let task = DispatchWorkItem { [weak self] in
DispatchQueue.global(qos: .userInteractive).async { [weak self] in
//Use search text and perform the query
DispatchQueue.main.async {
//Update UI
}
}
}
self.searchTask = task
//0.5 is the wait or idle time for execution of the function applyFilter
DispatchQueue.main.asyncAfter(deadline: DispatchTime.now() + 0.5, execute: task)
}updateSearchResults is the UISearchController delegate method which gets called on each key press.
searchTask has the property to store DispatchWorkItem. DispatchQueue executes the DispatchWorkItem closure after the deadline time 0.5s and if the method gets called before the deadline then the searchTask is invalidated and reinitialised.
RxSwift
RxSwift is a framework for interacting with the Swift programming language, while RxCocoa is a framework that makes Cocoa APIs used in iOS, easier to use with reactive techniques.
First you will have to add RxSwift and RxCocoa to the project. You could use Cocoapods or Carthage or Swift Package Manager to add these dependencies
//Import Rx dependencies
import RxSwift
import RxCocoa
//holds all the disposables
let disposeBag = DisposeBag()
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
applyRxSwiftSearch()
}
//Initialise the publisher and subscriber for search
func applyRxSwiftSearch() {
searchController.searchBar
.rx.text
.debounce(.milliseconds(500), scheduler: MainScheduler.instance)
.subscribe(onNext: { [unowned self] query in
DispatchQueue.global(qos: .userInteractive).async { [weak self] in
//Use search text and perform the query
DispatchQueue.main.async {
//Update UI
}
}
})
.disposed(by: disposeBag)
}Disposebag is used for memory management and it holds all the disposables and allows us not to have to dispose of each subscription individually
searchBar is wrapped to Rx and is subscribed to search text changes.
debounce() listens to user events and publishes if there is a delay of 0.5s in user activity.
Subscriber receives the event of the search text which then is queried against the actual records.
DisposeBag collects all the disposables.
Combine
Combine is Apple’s new reactive framework for handling events over time. Combine Framework is Natively supported from iOS 13 and Swift 5 onwards.
First you will have to import Combine Framework.
//Import Framework
import Combine
//holds all the cancellables
var cancellable = [AnyCancellable]()
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
applyCombineSearch()
}
//Initialise the publisher and subscriber for search
func applyCombineSearch() {
let publisher = NotificationCenter.default.publisher(for: UISearchTextField.textDidChangeNotification, object: searchController.searchBar.searchTextField)
publisher
.map {
($0.object as! UISearchTextField).text
}
.debounce(for: .milliseconds(500), scheduler: RunLoop.main)
.sink(receiveValue: { (value) in
DispatchQueue.global(qos: .userInteractive).async { [weak self] in
//Use search text and perform the query
DispatchQueue.main.async {
//Update UI
}
}
})
.store(in: &cancellable)
}Cancellable is a protocol indicating that an activity or action supports cancellation. It frees up any allocated resources. It also stops side effects such as timers, network access, or disk I/O.
Publisher publishes the events whenever there is a change in the text in searchBar.
debounce() listens to user events and publishes if there is a delay of 0.5s in user activity.
sink() collects all the cancellable activities.
Conclusion
The query happens only if the user activity is idle for 0.5s while entering the search text, in this way we would be limiting a lot of redundant queries which results in app being responsive.
Now we are left with a question. Which one to choose?
In my opinion, if you are using RxSwift or Combine in your projects then you already know what you should go for and if you aren’t then using RxSwift or Combine to achieve debounce is bit overkill, in which case you could achieve using Timer or DispatchWorkItem.
Please find the sample solution here: Github
Thanks for reading. Happy coding.